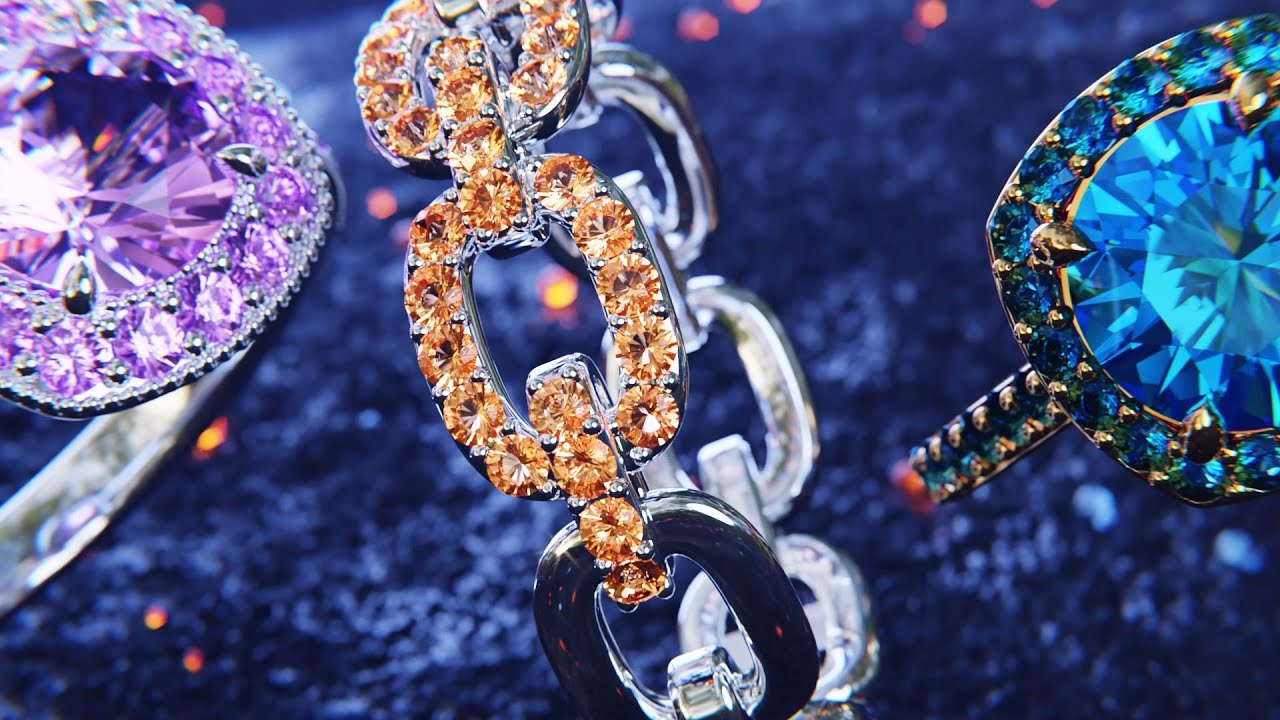Gemstones, often referred to as “gems” or “precious stones,” are natural minerals known for their beauty, durability, and rarity. For centuries, they have been cherished as symbols of wealth, power, and love, playing significant roles in cultures and traditions around the world. From the deep blue of sapphires to the fiery red of rubies, gemstones come in a vast array of colors, each with its unique story and allure.

The Formation of Gemstones
Gemstones are formed deep within the Earth under extreme conditions of heat and pressure. These natural processes cause certain minerals to crystallize over millions of years, resulting in the stunning stones we see today. The color, clarity, and other characteristics of a gemstone are influenced by the specific minerals and elements present during its formation.
Some gemstones, like diamonds, are composed of a single element (carbon, in the case of diamonds), while others, like emeralds, owe their color and properties to a combination of elements. The process of gemstone formation is complex and varies significantly between different types of stones, making each gemstone unique.
Types of Gemstones
Gemstones are typically categorized into two main types: precious and semi-precious stones. This classification is based on their rarity, value, and historical significance.
Precious Gemstones:
- Precious gemstones are the most valuable and sought-after stones. The four main types of precious gemstones are:
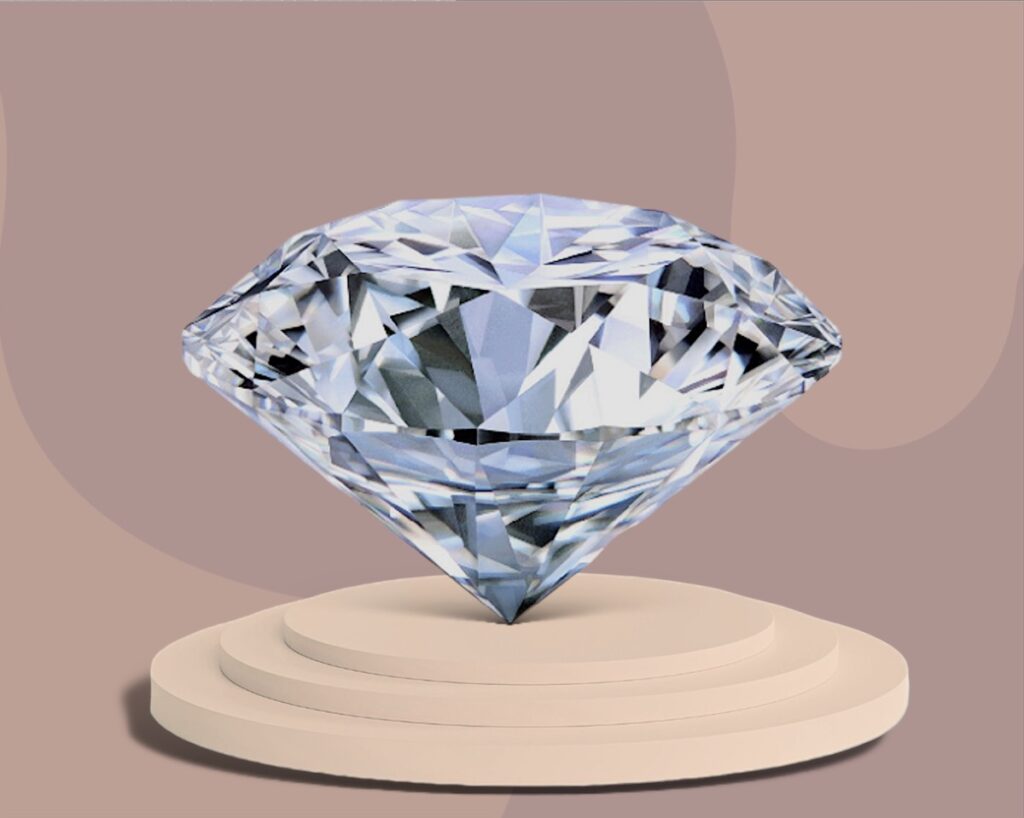
- Diamonds: Known for their unmatched hardness and brilliance, diamonds are the most famous of all gemstones. They are commonly associated with love and are the traditional choice for engagement rings.
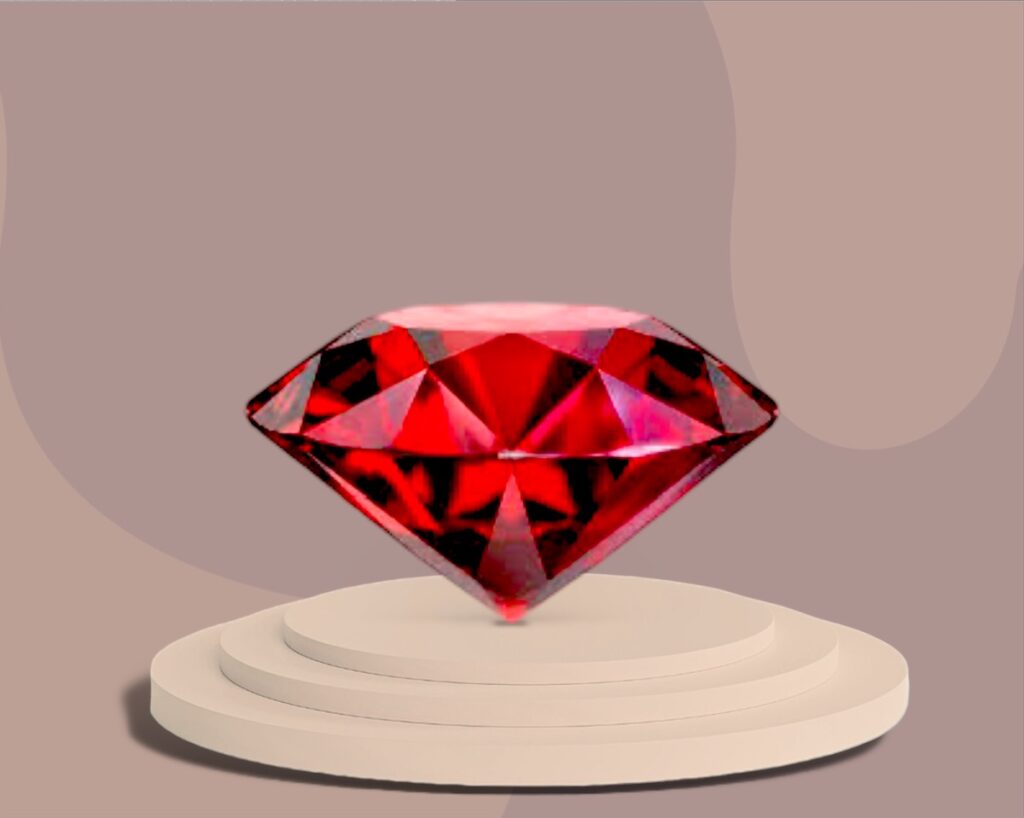
- Rubies: With their deep red color, rubies symbolize passion, love, and power. High-quality rubies are rarer than diamonds, making them highly valuable.
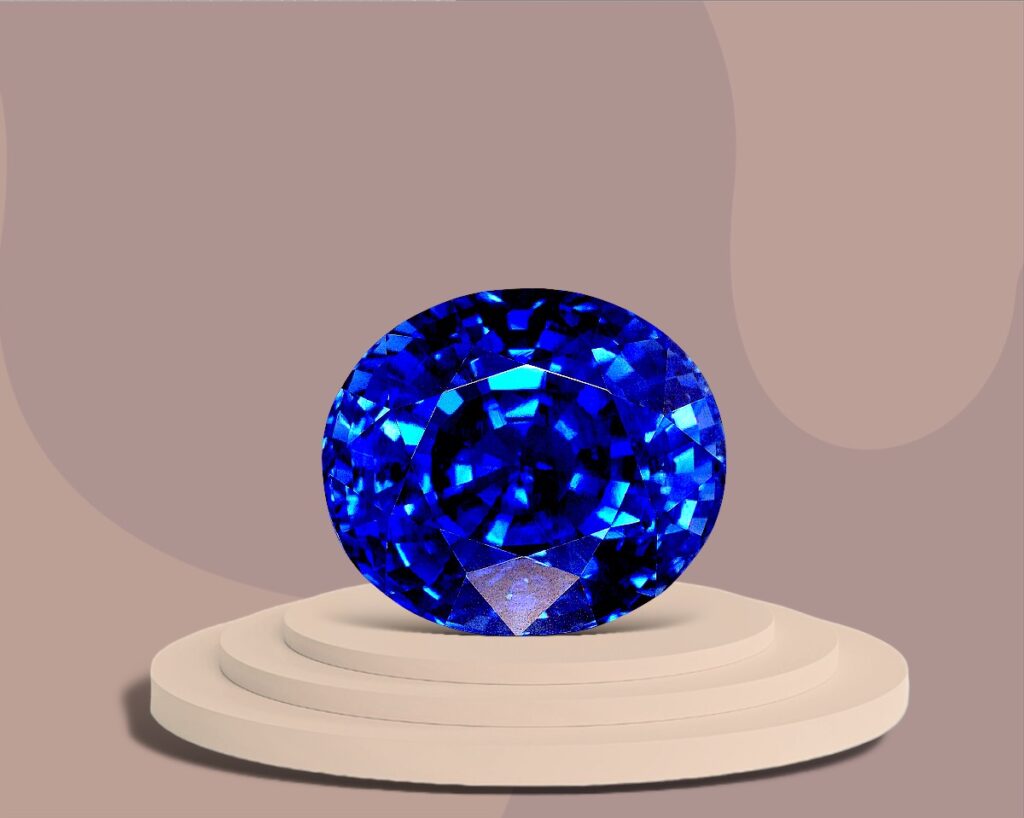
- Sapphires: Sapphires are best known for their vibrant blue color, although they can be found in a variety of other colors. They are symbols of wisdom, virtue, and good fortune.
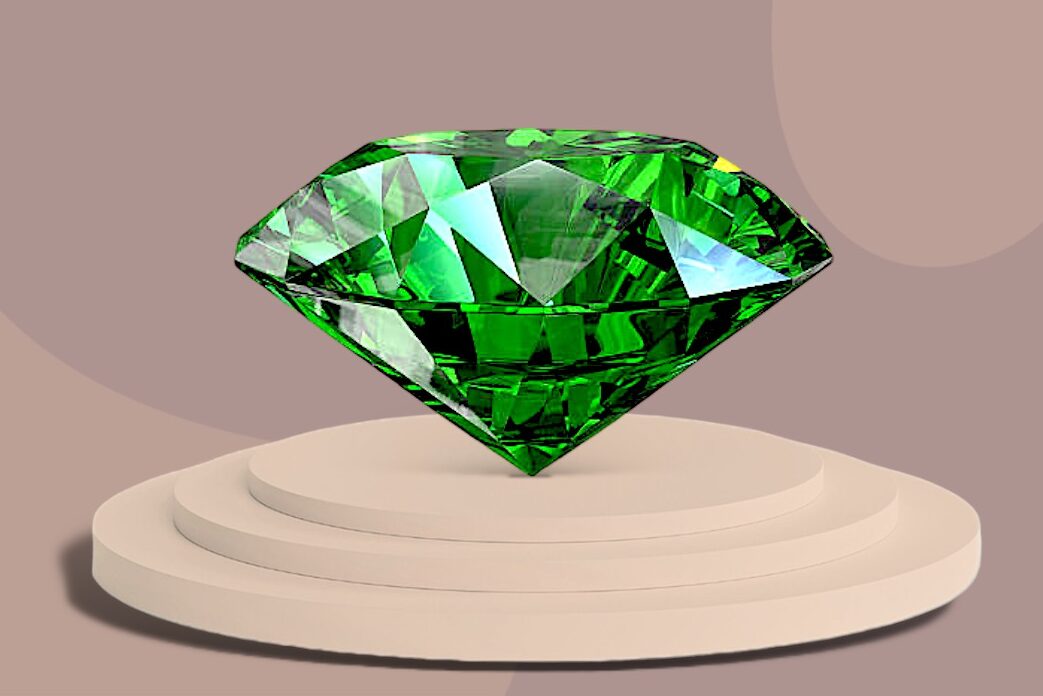
- Emeralds: Recognized by their rich green color, emeralds represent growth, renewal, and prosperity. They are one of the oldest known gemstones, with a history dating back thousands of years.




Semi-Precious Gemstones:
- Semi-precious gemstones are more abundant than precious stones and come in a wider range of colors and varieties. Some popular semi-precious gemstones include:
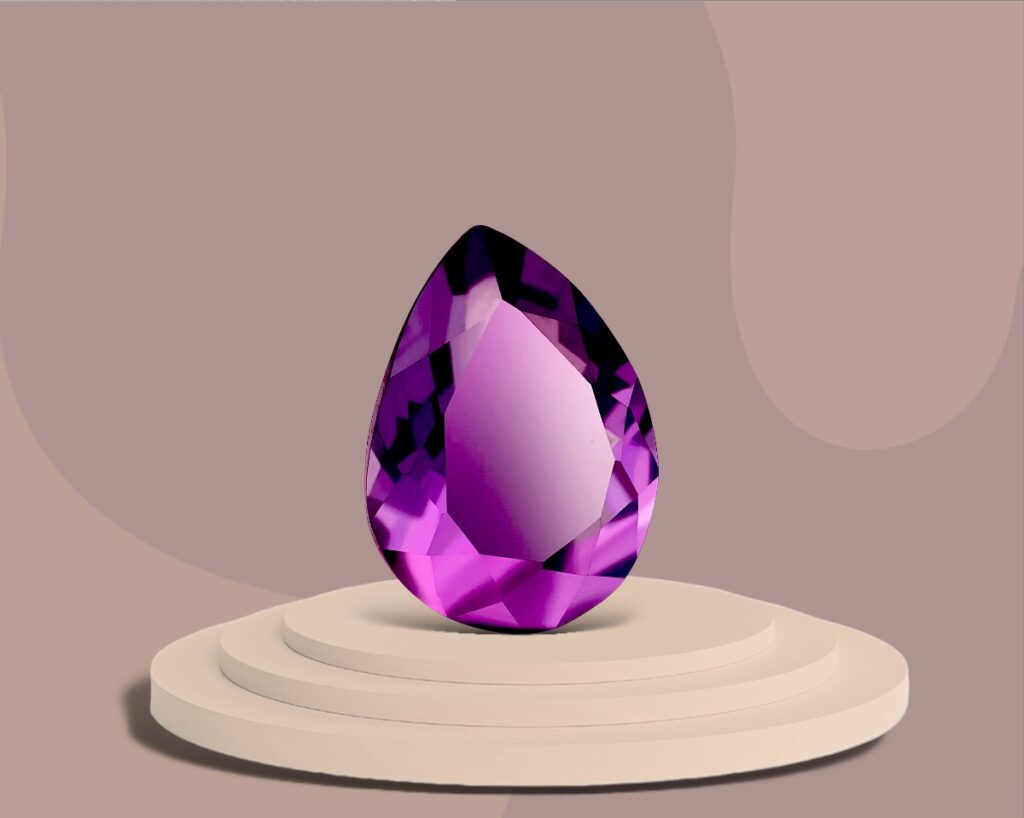
- Amethyst: A purple variety of quartz, amethyst is known for its calming and protective properties. It has been valued since ancient times for its beauty and supposed healing powers.
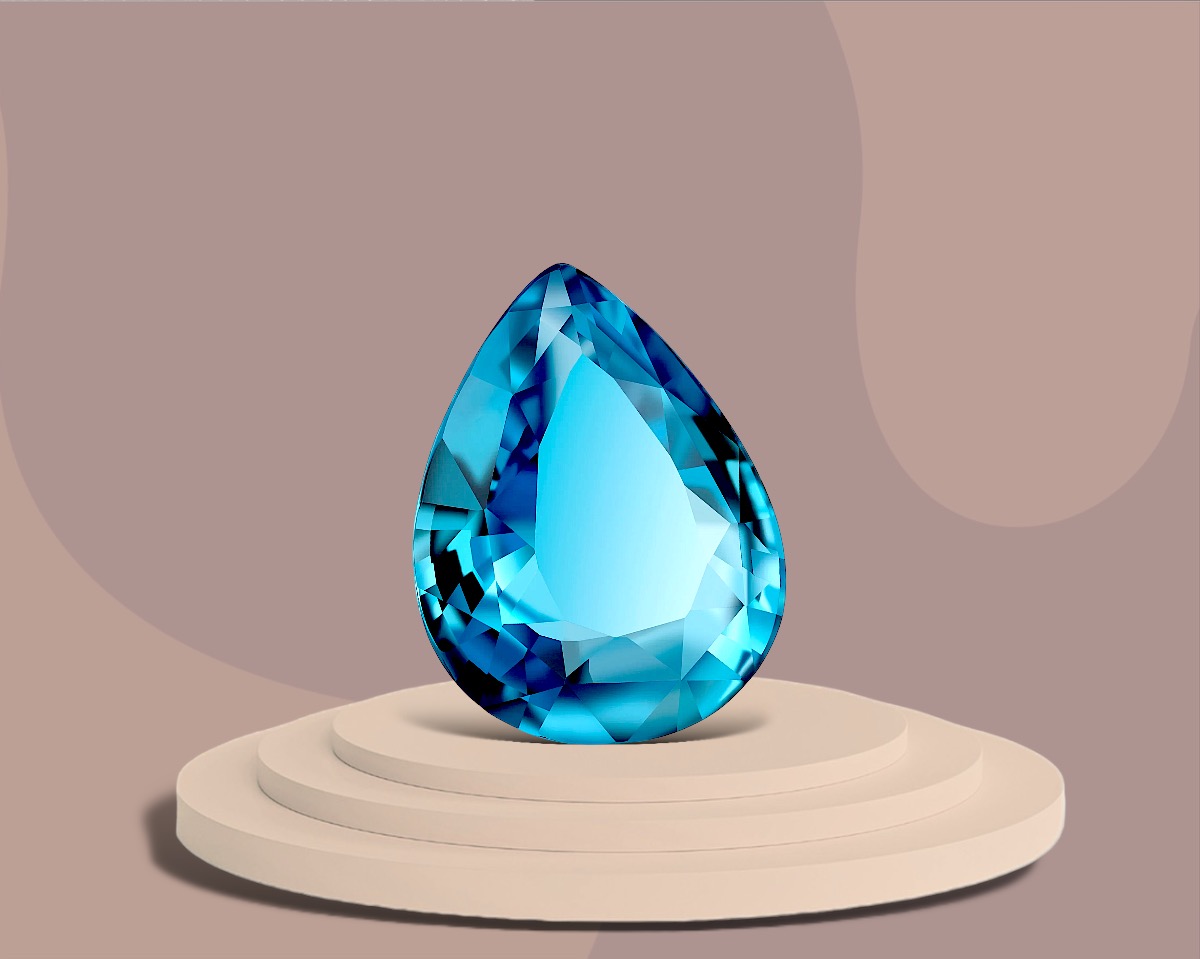
- Topaz: Topaz can be found in various colors, including yellow, blue, and pink. It is believed to bring strength and wisdom to its wearer.
- Aquamarine: This light blue to greenish-blue stone is associated with the sea and is thought to bring calmness, clarity, and protection.
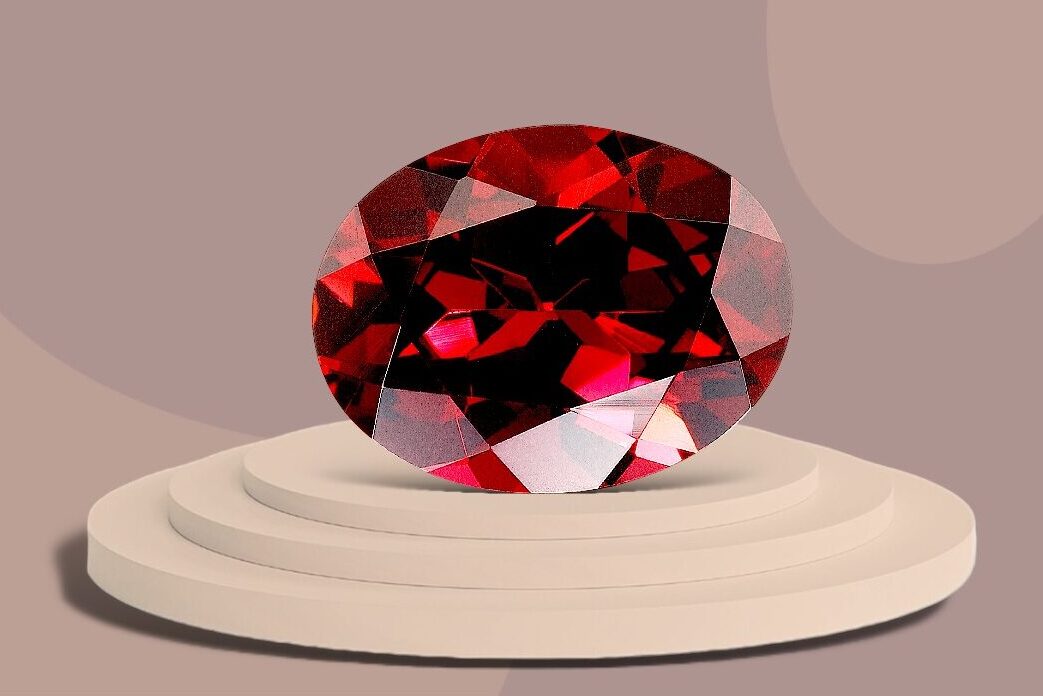
- Garnet: Available in a range of colors, garnet is often red and is believed to inspire love, passion, and creativity.




The Value of Gemstones
The value of a gemstone is determined by several factors, commonly known as the “Four Cs” for diamonds, but these principles can also apply to other gemstones:
- Color: The color of a gemstone is one of the most important factors in determining its value. The more vibrant and pure the color, the higher the value. For example, deep, saturated colors like the red of a ruby or the green of an emerald are highly prized.

- Clarity: Clarity refers to the presence or absence of internal or external flaws, known as inclusions and blemishes. Gemstones with fewer inclusions are considered more valuable, although some inclusions can add character to certain stones.
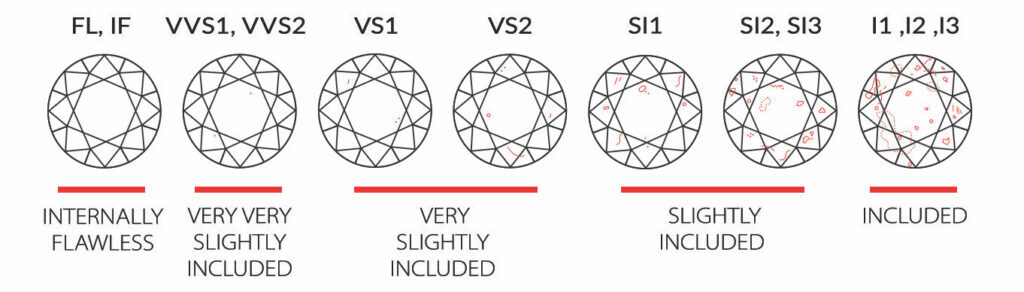
- Cut: The cut of a gemstone affects how it reflects light and displays its brilliance. A well-cut gemstone will sparkle and show off its color to its best advantage. The quality of the cut can significantly impact the stone’s value.
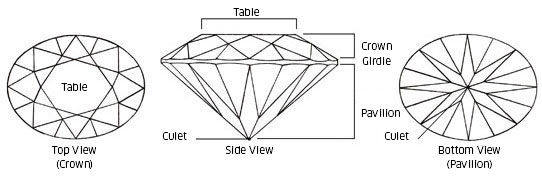
- Carat Weight: Carat weight measures the size of the gemstone. Larger gemstones are rarer and therefore more valuable, but the other factors (color, clarity, and cut) also play a crucial role in determining overall value.

Cultural and Symbolic Significance:
Gemstones have long been associated with various myths, legends, and symbolic meanings. Many cultures believe that gemstones possess special powers or energies that can influence the wearer’s life. For example, it is believed that emeralds bring wisdom and patience, while sapphires offer protection and spiritual insight.
Birthstones, a modern tradition with ancient roots, are gemstones associated with each month of the year. Wearing one’s birthstone is thought to bring good luck and protection. For example, January’s birthstone is garnet, symbolizing peace and prosperity, while April’s birthstone is the diamond, representing eternal love and strength.

Conclusion
Gemstones are not just beautiful pieces of nature but are also steeped in history, culture, and symbolism. Whether used in jewelry, collected as a hobby, or held for their believed metaphysical properties, gemstones continue to captivate people around the world. As with any valuable commodity, understanding the origin, quality, and ethical implications of gemstones is essential for making informed and responsible choices.